Seismic Methods are the geophysical methods, which can provide great information about stratigraphy, hydrogeology, and bedrock topography. Seismic surveys are a cost-effective way to extend information derived from borehole logs over a much larger area, minimizing the need for costly multiple borings. In comparison to pin point information derived from logs of boreholes, seismic surveys provide continuous information all along seismic survey lines at much cheaper rates, which makes the seismic surveys most economic tool for determining the sub-surface information.
There are various types of seismic surveys, which are used for different applications namely Seismic Refraction, Seismic Reflection, Seismic Tomography and Borehole seismic Survey. Seismic Refraction / Reflection Survey is generally used for soil stratification, hydrogeology and bedrock profiling. Crosshole seismic surveys are used to determine geotechnical properties of rock and soil.
In Seismic surveys acoustic waves are generated in the ground using a seismic source, travel time of the reflected/refracted energy waves traveling through the earth to return to the surface is measured and seismic velocities of the sub-surface material is determined by analyzing the data.
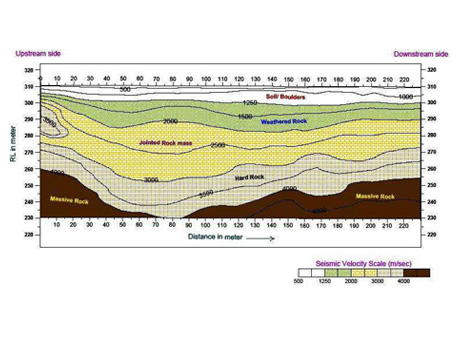
By analyzing and interpreting this data, it is possible to gain some understanding of characteristics of subsurface layers such as depth, thickness, and attitude, which is related to seismic velocities of sub-surface material.
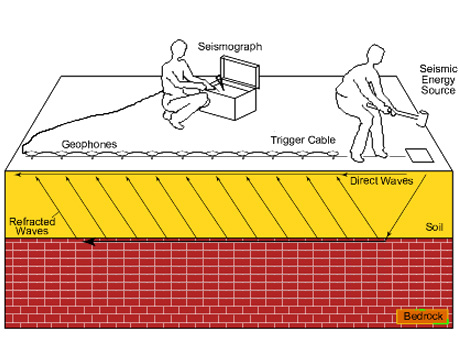
In seismic surveys, geophones are set out along a straight line and connected to the recording unit called seismograph. A seismic source, usually a weight drop or an explosive charge, generates an energy pulse. The time at which reflected or refracted signals are detected at each geophone is recorded on the seismograph. The time and distance data are then analyzed to determine the seismic velocities, which are finally interpreted for sub-surface material characterization.
ORIZON having extensive experience, state-of-the-art equipment, interpretation methods, and software is able to overcome the limitations of difficult site conditions and provide our clients with interpretations based on high quality data in extremely difficult conditions.
We use various interpretation methods to interpret seismic refraction data. These sophisticated seismic refraction interpretation technique has the following benefits:
Applications
The seismic refraction method is based on the measurement of the travel time of seismic waves refracted at the subsurface layer's interfaces due to dielectric contrast. Seismic energy is generated on surface by a source ('shot' using Hammer & Plate, weight drop or small explosive charge).
Read More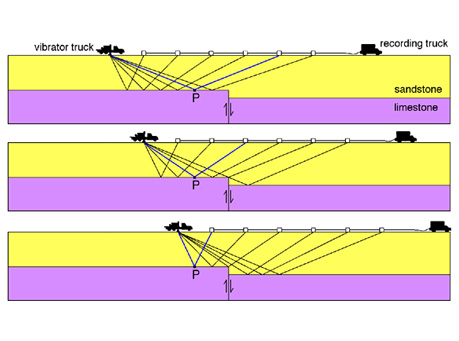
Deep seismic reflection surveying is the most advanced technique in geophysics today due to its major application for oil and gas exploration. This technique has other applications on a smaller scale, such as for civil engineering & infrastructure projects.
Read More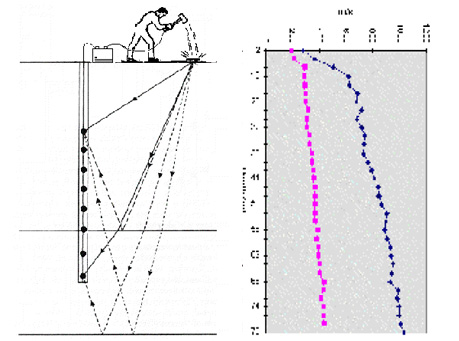
surface in increments down the borehole. Downhole seismic surveys are the simplest and cheapest method for borehole seismic techniques, as only one borehole is required for these surveys. Seismic energy is generated on surface at a fixed distance from the top of the borehole.
Read More